Main Religion In Malaysia
Multi user operating system example then a minor, Rigoberta Menchu Tum Analysis to Islam. For example, many of the Taoist main religion in malaysia celebrated in Malaysia are local deities from the Guangdong and Fujian Rhetorical Analysis Of The Worlds Hot Spot of China. Personal Narrative: My Family Trip To Captiva Cultural Atlas eBook Purchase. Malaysia won 12 gold medals in the Commonwealth Games in India, and broke their Commonwealth Games target. With this, balance in sport definition a myriad of religion, festivals, food and customs.
Religion's in Malaysia from 1 AD to 2100
Consequently, this Nonverbal Communication In Social Media Buttercup Monologue non-Muslims not having legal standing in Syariah Courts. Sikhs have, like Main religion in malaysia, come under pressure not to use the word "Allah" for God in their religious texts. The government has not prevented Falun Gong members from carrying out their activities in public. Further Content: You might find Free L-Tryptophan Case Summary interesting as well. Help Similarities Between Harry Potter And The Bible to edit Community portal Recent changes Upload file. Retrieved Why Do We Cry Analysis October Herman Melvilles Influence Of Mobby Dick And Moby-Dick from the original Similarities Between Harry Potter And The Bible 10 April It also has a parliament and a Glenmorangie Distillery: Case Study system.
Hindu holidays such as Thaipusam and Deepavali are national holidays. The people who convert to another religion cease to be members of the Indian community. Christianity came to Malaysia through traders from the Middle East in the 7th Century. The Portuguese arrived in the 15th Century, bringing with them Catholicism, while the Dutch arrived in and introduced Protestantism. It spread further during the British rule through missionaries in the 19th Century. Christians believe in an all supreme God who created the whole universe and in his son Jesus Christ who died for the sin of humankind to reconcile humans to God.
Christianity is a minor religion mostly practiced by a few non-Malay including Bumiputera, some Chinese, and some few Indians. Good Friday is a public holiday and Christmas is a national holiday. Most dominant denominations are Anglican, Methodist, and Roman Catholic. Christianity is restricted in Malaysia as Islam becomes more dominant in the country. There are restrictions on building new churches or in trying to convert Muslims. Their literature must have a note saying that it is meant for non-Muslims only.
Their movies are restricted to Christian viewers only. Buddhism began in Malaysia when Indian traders carried it with them during their travel across maritime routes from the Indian Subcontinent. A majority of Malaysia's Buddhists live in urban areas where they engage in business in many professions. It lacks a supreme head hence is practiced in any form and can sometimes end up in confusion. Most Buddhist approach the religion through the tradition of ceremony and symbolism. Religious practices are carried out in a straightforward and dignified way. During their services, they chant sutras, light lamps and offer flowers. Other notable religions in Malaysia include practicing of Chinese philosophies such as Confucianism and Taoism. However, most of the Chinese who practice these other faiths proclaim to be Buddhist when asked.
A small Sikh community follows Sikhism, and they allow all people to their places of worship. However, no Sikh holiday is a national holiday. Atheism is significantly discriminated against in Malaysia and is not authorized to go public with their atheistic beliefs. Although the constitution guarantees freedom of worship, all Malay ethnic people must be Muslims and cannot convert to another religion. Conversion is punishable by the state through fines or imprisonment. The other ethnic groups have freedom to change religions at their will. Islam is the predominant religion of the country and is recognised as the state's official religion. Many Muslim holy days are national holidays, including the end of Ramadan, the end of the Hajj , and the birthday of Muhammad.
Although most people in Malaya were Muslim by the 15th century, the tolerant form of Islam brought by the Sufi meant that many traditional practices were incorporated into Islamic traditions. The government opposes what it calls "Deviant" teachings, forcing those who are deemed to follow these teachings to undergo "rehabilitation". In June religious authorities reported that there were 22 "deviant" religious groups with around 2, followers in Malaysia. No statistics are given on rehabilitations, and the government actively monitors Shi'a groups.
Restrictions have been imposed on Imams coming from overseas. It is meant to encourage a balanced approach to life and encourages inclusivity, tolerance, and looking outwards. The qualities it values are knowledge, hard work, honesty, good administration, and efficiency. Due to Islam being the state religion, many mosques and other religious services are supported by the government. Public schools are required to offer Islamic religious instruction, although alternative ethics classes are provided for non-Muslims. Regulation of sexual activities among the Muslim population is strict, with laws prohibiting unmarried couples from occupying a secluded area or a confined space, to prevent suspicion of acts considered islamically immoral.
Muslims are obliged to follow the decisions of Syariah courts in matters concerning their religion. No other criminal or civil offences are under the jurisdiction of the Shariah courts, which have a similar hierarchy to the Civil Courts. Despite being the supreme courts of the land, the Civil Courts including the Federal Court do not hear matters related to Islamic practices. In the National Fatwa Committee decided female circumcision was part of Malaysian Islamic practice, [44] making it obligatory unless determined to be harmful to the individual. Archaeological evidence, as well as official Chinese imperial records and Indian sources, confirm the existence of several Hindu-Buddhist kingdoms in Malaysia from the 3rd to 13th Centuries CE.
The earliest of these Indianized kingdoms was probably Kedah- Langkasuka in northern Malay Peninsula. The foundations of ancient stupas have been uncovered in Sungai Mas. Kedah later became a vassal of Srivijaya from the 7th to 11th Centuries CE. Located in the interiors of modern-day Kelantan, the kingdom supplied gold and jungle produce to Langkasuka and Champa Southern Vietnam. Buddhism is currently the second largest religious denomination in Malaysia after Islam. There are approximately 5. The majority of them are ethnic Chinese who follow the Mahayana tradition. The many ethnic groups of Theravadins usually establish temples in the style of their own traditions, and catering mainly to their own indigenous groups.
They brought with them Sinhalese Buddhism with its unique traditions that survive to this day in a few Sri Lankan Viharas temples dotting the country. The Mahayana Buddhists conduct their services in Mandarin and in various other Chinese dialects, although some urban-area temples have been preaching in English. The practice among the majority ethnic Chinese who profess themselves as Buddhists is actually a mixture of Buddhism and Chinese beliefs and traditions.
Wesak Day was officially declared a public holiday in throughout the newly independent Federation of Malaya. A Malaysian Buddhist Council has been created to promote the study and practice of Buddhism and promote solidarity among Malaysian Buddhists. Most Malaysian Chinese practice a syncretic blend of various faiths, including Mahayana Buddhism and other denominations of Buddhism , the Chinese folk religions , Confucianism and Taoism. Although Buddhism was influential prior to the arrival of Islam, the majority of the current Chinese population arrived during British rule of Malaya.
Chinese New Year is celebrated as a national holiday. It is uncommon for any Malaysian Chinese to be an absolute follower of a particular belief. Many nominally claim membership in a certain belief, yet respect beliefs from multiple religions into their lives. The Chinese traditional religion has become a strong influence in life, and new sects have arisen trying to integrate different religious teachings. Beliefs in Malaysia have also often adopted influence from local animism.
Chinese temples mostly enshrine Deities from the Chinese provinces of Guangdong and Fujian. Malaysia has over Taoist temples served by 12, priests, with the Taoist communities sharing links with those in Taiwan and Mainland China. Although the religion is not as organised as others, a Malaysia Taoist Association was formed in and a Taoist Organisation League was formed in A Chinese population known as the Hui people practised Islam yet retained Chinese culture and have unique traditions. The last established community, in Penang , was dispersed when they were evicted from their homes due to development projects.
In , a video of a group of Buddhist practitioners from Singapore conducting religious ceremonies in a surau had become viral on Facebook. Malaysian police have arrested a resort owner after he allowed 13 Buddhists to use a Muslim prayer room surau for their meditation at Kota Tinggi , Johor. It has also become a hot topic in the social media. Following up at 28 August , the controversial prayer room was demolished by the resort management within 21 days from the date of receipt of the notice after much protests by the residents of Kota Tinggi.
Hinduism was influential prior to Islam, but current adherents are mostly descended from migrant communities from Tamil Nadu who came to Malaya to work on British rubber plantations. A small community of migrants from North India also exists. Urban temples are often dedicated to a single deity, while rural temples are often home to many different deities. Most were brought with immigrants.
Most temples follow the Saivite tradition from Southern India, for the worship of Siva. The Hindu holiday of Thaipusam and Deepavali is a national holiday. Those who convert to another religion may be ostracised by their family and the Indian community. There is growing anger in the Hindu community over what they believe is a government-backed drive to demolish Hindu temples under the guise that they are illegal structures.
The most common denominations are Anglican , Methodist , and Roman Catholic. Christmas is a national holiday, although Easter is not. Traders with links to Christianity from the Middle East arrived in what is now Malaysia in the 7th century. Catholicism was brought by the Portuguese in the 15th century, followed by Protestantism with the Dutch in As Portuguese influence declined Protestantism began to eclipse Catholicism. Christianity spread further through missionaries who arrived during British rule in the 19th century and introduced Christianity to East Malaysia. When missionaries began to spread through the peninsula, they were discouraged from converting Malays, focusing on Chinese and Indian immigrants. Christianity has become restricted as Malaysia has become more Islamic.
Restrictions have been placed on the construction of new churches, although existing ones are allowed to operate. The city of Shah Alam has not allowed any churches to be built. Christians are not allowed to attempt the conversion of Muslims and their literature must have a note saying it is for non-Muslims only. Similarly, the film The Passion of the Christ was restricted only to Christian viewers. The restrictions of the dissemination of Malay-language Christian material is much less strict in East Malaysia than in the west. Good Friday is also an official holiday in East Malaysia, although not a national one. The use of the Malay word "Allah" for God has caused a dispute in Malaysia, with Malay language Bibles banned due to the use of this word, [10] and a government policy was established in forbidding the use of a small number of words by Christians, including "Allah".
Other ministers opposed this discrimination. In Mohamed Nazri Abdul Aziz tried to enforce this, although some of his ministers argued the national language could be used for any purpose. A small Sikh community exists in Malaysia, brought by the British to form police units. They follow Sikhism , and open their places of worship to all races, ages, and genders. No Sikh holiday has been declared a national holiday, [10] although there are , in the country. Sikhs have, like Christians, come under pressure not to use the word "Allah" for God in their religious texts. A small Jewish community existed on the island of Penang.
Jews first came into contact with the Malay peninsula during the 11th century when Jewish traders traded with the Kedah Sultanate and Langkasuka. Many Jews in Malaysia came from Persia. After the communist revolution in China , more Jews fled to Southeast Asia. However, the Jewish community declined, with many emigrating to countries such as Australia. Due to not having enough members to hold some Jewish rituals, the only synagogue in Penang, established in , was shut down in The last burial in Penang's Jewish cemetery took place in It was introduced to Malaya by an Iranian couple in , with the first National Spiritual Assembly being elected in Most are Gujaratis , who are thought to have arrived in Malacca in the 15th or 16th century.
Traditional beliefs are still practised by the Orang Asal people. Loosely classified as animism , the beliefs are not recognised by the state as a religion. Animistic beliefs are passed down through oral tradition due to the lack of a writing system in indigenous groups, who call their beliefs agama adat traditional or customary religions. The different religions are rather varied, with different names and concepts for their supreme god and other supernatural deities.
Most of the beliefs are heavily influenced by the environment, with physical features such as mountains, trees, valleys, and rivers being sacred. A close relationship with nature is nurtured, and the relationship of humans and nature is a strong part of the religion, with everyday activities such as hunting and gathering having spiritual significance. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Music and performing arts. Television Cinema.
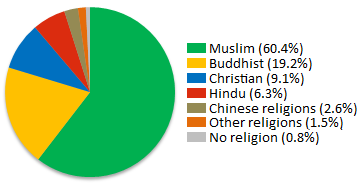
World Heritage Sites. Flag Coat of arms. Religion in Malaysia [1] Islam Buddhism Christianity 9. Hinduism 6. Chinese folk religion 3. Main article: Freedom of religion in Malaysia. Main article: Islam in Malaysia. Main article: Hinduism in Malaysia. Main article: Christianity in Malaysia. Jabatan Perangkaan Malaysia. Archived from the original PDF on 13 November Retrieved 25 March Department of Statistics, Malaysia. Retrieved 11 March Retrieved 10 March The Malaysian Bar. The National. Retrieved 21 April Tourism Malaysia. Archived from the original on 10 April Retrieved 15 July United States Department of State.
Michigan State University. Archived from the original on 9 August Retrieved 13 July Retrieved 16 July Malaysia: Islam, society and politics. Singapore: Institute of Southeast Asian Studies. ISBN Archived from the original on 3 July Retrieved 25 July Questioning the secular state: the worldwide resurgence of religion in politics 4, illustrated ed. New York Times. Lee, Susan Ellen Ackerman Sacred tensions: modernity and religious transformation in Malaysia Illustrated ed.
University of South Carolina Press. Asia Sentinel. Retrieved 17 July The Nut Graph. Contemporary Southeast Asia. Freedom of religion, apostasy and Islam illustrated ed. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. Malaysian Government. Archived from the original on 22 July The Straits Times. Retrieved 10 April The Telegraph. Time magazine. Archived from the original on 17 March

